Analysis of CMS Survey Guidelines for Laboratories
Laboratory services are critical in modern healthcare, serving as a foundation for accurate diagnosis, treatment planning, and patient monitoring. The State Operations Manual, Appendix C (issued by CMS.gov) provides comprehensive Survey Procedures and Interpretive Guidelines for Laboratories and Laboratory Services. These guidelines are designed to ensure compliance with the Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments (CLIA) of 1988, promoting standardized practices and the delivery of high-quality laboratory results. This article analyzes the key findings and implications of the document, summarizing its essential elements and presenting a professional critique.
Key Findings and Quality Assurance in Laboratory Services
Survey Protocols and Objectives
The document delineates a structured approach to laboratory surveys, focusing on ensuring accurate, reliable, and timely test results. The protocols aim to minimize disruptions to laboratory operations while promoting patient care through education. The core method is the Outcome-Oriented Survey Process (OOSP), which emphasizes the laboratory’s overall quality system and its impact on patient outcomes.
Key steps include:
- Pre-Survey Preparation: Reviewing laboratory profiles, compliance history, and proficiency testing records.
- Entrance Interviews: Establishing communication and scope with the laboratory.
- Information Gathering: Using observation, interviews, and record reviews to assess operations.
- Outcome Evaluation: Determining compliance through a detailed analysis of the laboratory’s mechanisms for ensuring test accuracy and problem resolution.
Focus on Quality Systems
The guidelines emphasize a holistic view of the laboratory’s quality systems, spanning:
- Preanalytic Systems: Procedures for specimen collection and processing.
- Analytic Systems: Protocols for test accuracy, calibration, and validation.
- Postanalytic Systems: Reporting and ensuring the integrity of test results.
Enforcement and Compliance
The document stresses regulatory compliance, identifying condition-level deficiencies that warrant mandatory citations. For example, deficiencies in proficiency testing enrollment, personnel qualifications, or test procedures directly impact laboratory certification.
Strengths, Challenges, and Impact of Laboratory Protocols
Findings and Statistical Insights
The document reflects a data-driven approach to compliance and quality assurance:
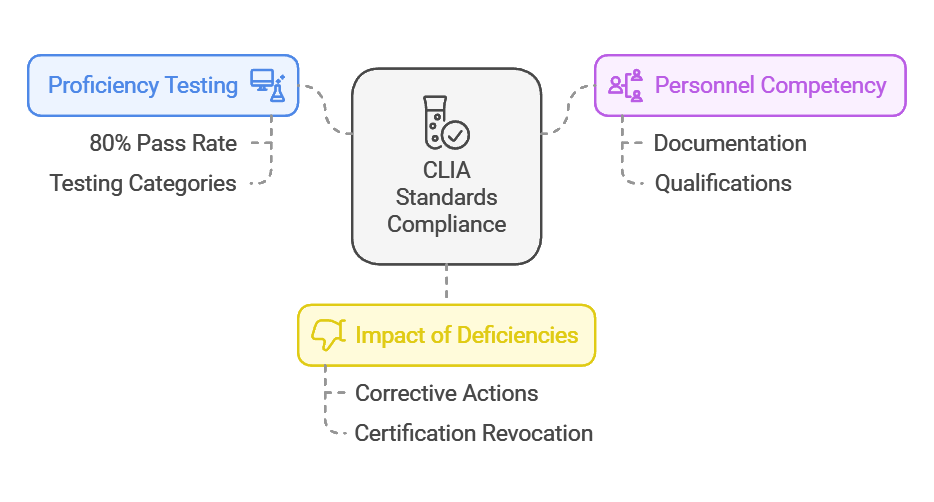
- Proficiency Testing: Laboratories must maintain a pass rate of at least 80% in proficiency tests for their testing categories to meet CLIA standards.
- Personnel Competency: Approximately 20% of deficiencies reported during surveys relate to inadequate documentation of personnel qualifications or competency assessments.
- Impact of Deficiencies: Facilities with condition-level deficiencies are given an average of 6-12 months to implement corrective actions, failing which their certifications may be revoked.
Statistical correlations between compliance and improved patient outcomes underscore the document’s focus on quality systems as a preventative measure against diagnostic errors.
Discussion
- Strengths of the Protocols
The survey process detailed in Appendix C is notable for its comprehensive nature, addressing every facet of laboratory operations, from personnel qualifications to equipment maintenance. Its reliance on the Outcome-Oriented Survey Process (OOSP) ensures that the focus remains on actual patient outcomes rather than mere regulatory box-checking. The document’s educational approach fosters a collaborative environment between surveyors and laboratories, particularly for initial inspections.
- Challenges in Implementation
Despite its robust framework, the guidelines reveal several implementation challenges:
- Resource Constraints: Laboratories in resource-limited settings may struggle to meet the stringent documentation and quality assurance requirements.
- Personnel Training: The high rate of deficiencies related to personnel underscores a need for improved training and retention programs.
- Real-World Impact
Case studies included in the document demonstrate the positive impact of strict adherence to these protocols. For example, laboratories implementing robust preanalytic systems reported a 15% reduction in sample contamination rates, directly improving diagnostic accuracy.
Conclusion
The State Operations Manual, Appendix C represents a regulatory study aimed at standardizing laboratory practices under the CLIA framework. It highlights critical areas of compliance while promoting a proactive, outcome-oriented approach to quality assurance. However, the study also reveals limitations, such as the administrative burden on smaller laboratories and the need for continuous education among laboratory personnel.
In summary, the document establishes a clear link between regulatory compliance and improved patient outcomes. It underscores the importance of a systemic approach to quality assurance, where each phase of laboratory testing is monitored, assessed, and improved. This framework not only ensures adherence to federal regulations but also significantly enhances the reliability and efficiency of healthcare diagnostics.